What Actually Is an Abscessed Tooth?
Abscessed tooth—also known as dental abscess—, is a term to describe any forms of pocket of pus (and blood) that can form in different parts of your gums and teeth. The abscess can cause sensitivity and mild to severe pain in the affected area, which can extend—in some cases— to your neck, ear, and jaw.
Dental abscess, when left untreated, can develop into various complications, some of them are life-threatening. Bacteria can spread into the bones near the infected area, which can cause the condition we call osteomyelitis—bone infection—. The infection can travel to other bones, as well as other organs. Also, an abscess can cause a blood clot in the sinuses, among other complications.
If you are suffering from an abscessed tooth, it is very important to call your dentist immediately and plan a suitable treatment.
The Different Types of Dental Abscess
Above, we have briefly discussed that there can be various places surrounding the teeth and gums where abscessed tooth can occur. Thus, there are several different types of abscessed tooth based on where the infection happens:
- Gingival abscess: abscess on the gum tissue, where the infection is not affecting the tooth and surrounding ligament.
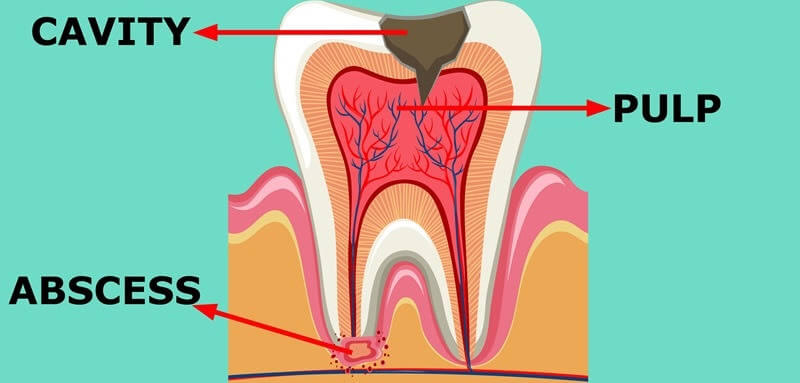
- Periapical abscess: chronic infection located at the tip of the tooth’s root, creating a pocket of pus near the jawbone. Periapical abscess commonly happens when the tooth is severely infected and the pulp/root is already dead.
- Periodontal abscess: abscess next to the tooth’s root or pulp. Less common that periapical abscess, and commonly happens when the tooth is still alive/vital tooth.
- Pericoronal abscess: The abscess occurs near the crown of a tooth.
In severe cases, abscesses can happen in multiple areas surrounding the same tooth, creating a combination of periapical and periodontal abscesses.
Symptoms of Dental Abscess
Here are some common signs and symptoms of a tooth abscess:
- Persistent toothache (often severe) that can extend to the ear, neck, or jawbone
- Sensitivity to hot and cold, as well as the pressure of normal chewing
- Swelling in your cheek or face
- Swollen lymph nodes under your jaw
- Fever, difficulty breathing or swallowing
- When the abscess ruptures, you might have a salty, foul-smelling fluid in your mouth. Worth noting that when the abscess ruptures, the associated pain might be relieved, but you will still need a dental treatment or the abscess might relapse.
- A visible pocket of pus (and blood) on your gum
- Puffy, tender gums
- Bad breath, and foul-smelling odor when you chew with the infected tooth
Cause of Tooth Abscess
Abscess happens when bacteria invade the tooth, gums, and especially the tooth’s pulp—the root, innermost part of the tooth where nerves and blood vessels are located— Bacteria can enter when the tooth is decayed, causing a cavity or crack, causing infection.
There are several factors that can increase the risk of a tooth abscess:
- Your diet- Foods and drinks high in sugar will increase the acidity in your mouth—the enzyme released to break down sugar is acidic—, which can contribute to tooth decay and cavities. Coffee consumption and a smoking habit can also increase the risks of cavities.
- Poor dental hygiene- Not regularly brushing and flossing your teeth, as well as getting your teeth cleaned regularly by the dentist can encourage plaque buildup, which can lead to tooth decay, gum diseases, and abscess, as well as other health issues.
- Dry mouth-A dry mouth will cause your teeth to be more brittle, making it easier to crack. Certain medications can cause a dry mouth, as well as aging issues.
How To Prevent Tooth Abscess
The key to preventing tooth abscess is to avoid tooth decay, which can be achieved by maintaining good oral hygiene practice:
- Brush your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and proper toothbrush. Do not brush your teeth right after eating—spare 10-20 minutes—, or rinse your mouth first to decrease acidity.
- Floss at least once a day, or you can use various alternatives to clean the spaces between your teeth.
- Drink fluoridated water
- Maintain a healthy diet, stop smoking, avoid consuming too much coffee and high-sugar foods/drinks.
- Replace your toothbrush regularly. A good practice is to replace your brush whenever the bristles are frayes—every three months or so—
- Rinse your mouth with a fluoride mouthwash, this can help protect your teeth from decay
Possible Treatments for Dental Abscess
There are several possible treatments in the case of a dental abscess, depending on the types of abscess (discussed above) and severity of the case. The goal is to completely cure the infection, and here are some possible treatments:
- Tooth Extraction- The dentist will extract the tooth and then drain the pus to get rid of the infection. This alternative is commonly done when the infected tooth is beyond saving—or already dead—.
- Drain The Abscess- If the tooth is still alive and can be treated (i.e. a crown or a filling), the dentist will make a small incision into the abscess and drain out the pus. Various methods can be done to drain the abscess, and after it’s all clean, the area will be washed with a saline solution.
- Root Canal- Performed when the tooth is already dead or can’t be saved, but the structure can still be maintained. The dentist will drill the tooth and remove the pulp, and then drain the abscess. The gap left will be sealed.
- Antibiotics might be prescribed to prevent the spread of the infection, or when you have a weakened immune system.
End Words
It’s important to understand that an abscessed tooth won’t heal by itself, and when left untreated the infection can spread—and might lead to sepsis, a life-threatening condition where the infection spreads throughout your body—.
Call your dentist immediately if you have any signs or symptoms of an abscess. If you can’t reach your dentist due to severe fever and difficulty breathing, go to the nearest emergency room—this is often the sign that the infection has spread further—
