Fat-Soluble Vitamins: Non Essential Vitamin List For Healthy Living
Do you know about vitamins? Also, do you know about fat-soluble vitamins? First I should tell you what is vitamin? Vitamins are necessary micronutrients that required for your body. They are a necessary nutrient to maintain your health.
Vitamins are categorized into two units one is a fat-soluble vitamin and another is water-soluble. It is easy to understand but difficult to manage the requirement of the vitamin in the human body. Here is a brief about fat-soluble and water-soluble vitamin.
Fat-Soluble Vitamins

Fat-soluble vitamins are types of vitamins that are exploited into the body through fatty tissue. If the fat-soluble vitamins such as A, D, E, and K are collect into your body for a long time. In this situation, it may be harmful to your body, comparison to water-soluble vitamins. Because enough amount of vitamins A required for good health. If you eating a balanced diet will not lead to toxicity in otherwise healthy individuals. Because, the majority of vitamins A, D, E and K can increase the toxicity of your body.
Fat-soluble Vitamins list
Fat-soluble vitamins are non-essential vitamins because they get absorbed fat and stored in the fatty tissues of the body. Here is the list of fat-soluble vitamins types-
- A
- D
- E
- K
All type of vitamin plays an important role in a living body, they act as promoters for a biological reaction. Deficiency of vitamin may cause a serious issue for your health.
Different type of fat-soluble vitamins works in your body different task. The fat-soluble vitamins may be necessary for the person who has lower because it can supply fat-soluble vitamins. But, an insufficient amount of fat-soluble vitamins in your body which could lead to toxicity and adverse reactions.
Suggested Blog-What Actually Is an Abscessed Tooth?
Vitamin A

- This is Vitamin A
Vitamin A is fat-soluble-vitamin. It is a necessary vitamin for maintaining healthy vision. Because, lack of vitamin A affects visibility, hair loss, and blindness.
Type
Vitamin A is not an element it is a compound. Vitamin A is known as retinoids. retinoid is a collection of the various component that found in the human body also in some food materials.
Function
Vitamin A has multiple functions or tasks in your body: it is necessary for development, for the maintenance of the immune system and well vision.
Dietary sources

- Dietary sources
Some dietary natural source of vitamin A such as
- fish liver oil
- liver of animals
- Butter
- Cod liver oil.
- Eggs.
- Fortified breakfast cereals
- Fortified skim milk.
Above dietary natural source are supplementary of Vitamin A. Besides it some fruits are a good source of vitamin A. You can readout.
- Carrots
- Sweet potatoes
- Winter squash
- Cantaloupe
- Apricots
- Spinach
- Kale
- collard greens.
Recommended intake
A dose of vitamin depends on human age and gender. You can take the following dose of fat-soluble vitamin A.
- Infants (0–12 months): 400–500 micrograms (mcg)
- Children aged 1–3: 300 mcg
- Children aged 9–13: 600 mcg adult
- Women: 700 mcg
- Adult men: 900 mcg
Deficiency diseases of vitamin A

- diseases of vitamin A
As you know that vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin. It is required for the body in limit amount neither nor more nor less. The factuality of vitamins can increase many problems. You can read b
- Hair loss
- Dry eyes
- Blindness
- Reduced immune function
- Skin issues
Overdose
It is possible to big toxic levels of vitamin A. This situation is called hypervitaminosis. People who diet vitamin A supplements or eat enough amounts on fish liver oils are at more risk. Pregnant women should not enough doses of on their prenatal vitamins. High levels of vitamin A are harmful to a growing embryo.
Vitamin D

- Medicine of Vitamin D
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin. An important source vitamin a is sunlight because, when the sunlight exposure on your body skin then a combination of sunlight and skin produce vitamin D. Vitamin D is a helpful source of bone health and development.
Type
Vitamin d knows as calciferol. It is not an element it is a compound like a vitamin A. It is a fat-soluble vitamins. Vitamin D is found in two types naturally.
- D-2 found in plants, such as mushrooms.
- vitamin D-3, found in animal fats vitamin.
The function of vitamin D
Your body must contain vitamin D to absorb Ca (calcium) and promote bone growth. Because lack of vitamin D results in soft bones in children (rickets) and fragile, misshapen bones in adults (osteomalacia). Vitamin D is necessary for other important body functions. Vitamin D helps to absorbed into the bloodstream, the liver and kidneys change calciferol into calcitriol etc. When you take vitamin D it performs to type major work.
- Bone maintenance
- Immune system support
Dietary sources of vitamin D

- Dietary sources of vitamin D
There are many sources of the fat-soluble vitamins, besides sunlight. The following food materials and natural product are supplementary of vitamin D.
- Fatty fish like tuna, mackerel, and salmon
- Dairy products
- Orange juice
- Soy milk
- Beef Liver
- Cheese
- Egg yolks
Recommended intake
According to your body age, you can take the value of vitamin D. Some basic guidelines to take the amount of vitamin D.
- Baby (0–12 months)10 mcg
- 1–70 years of age 15 mcg
- above age 70: 20 mcg
Diseases, lack of vitamin D

- Diseases of vitamin D
There are many problems may be lack of vitamin D. I want to tell you some problem of vitamin D.
- Rickets Rickets
- Osteoporosis
- Heart disease
- Lupus
- Diabetes
Overdoes of Vitamin D
Venom levels of vitamin D probably occur. They are most likely to occur in people who take an insufficient amount of vitamin D supplements. Due to hypercalcemia, maybe increased the amount of vitamin D.
Vitamin E

- E: Vitamin
Vitamin E is a type of vitamin but it does not soluble in water. It is a fat-soluble vitamin. Vitamin E likes work in your body an antioxidant. It can remove or destroy free radicals in your body. Because free radicals may be the cause of cancer. Vitamin D has plays an important role to control cancer disease.
Type
Vitamin D can divide into eight types. but mainly two types is vitamin E first tocopherols and second tocotrienols. Vitamin E is contained the most abundant in Tocopherol.
The function of Vitamin E
Vitamin E is antioxidant, protects fatty tissues from free radicals that may cause cancer. Water-soluble vitamins like vitamin B complex and vitamin c, help aid vitamin E’s functions. If you have taken higher doses of vitamin E it can do help thinner of the blood in your body.
Source of vitamin E

- Source of vitamin E
There are many sources of vitamin E which you can read out also with you can use in your diet.
- Wheat Germ Oil
- Sunflower Seeds
- Almonds
- Pine Nuts
- Goose Meat
- Crayfish
- Hazelnuts
Recommended Intake
You can take the amount of vitamin E according to your age. The following doses of vitamin E can eat in your diet.
- Baby aged 0-6 Month: 4 mcg
- Baby aged 7-12 Month: 5 mcg
- Children aged 1-3 year: 6 mcg
- Children aged 4-8 year: 7 mcg
- A boy aged 9–13 years: 11 mcg
- Above 14 years: 15 mg
- For younger: 19 mg
Symptoms lack of vitamin E
- Vision issues
- Loss of weight also with slow growth.
- Trouble walking muscle weakness
- Tremors
- Fragile red blood cells
Vitamin K

- Medicine of Vitamin K
Vitamin K is fat-soluble vitamins and it helps the body form blood clots. This requires function prevents a person from bleeding out from small scratches.
Type
Vitamin K is a various type but major are two types of vitamin k.
- K-1, found in plant sources
- Vitamin K-2 found in animal sources
A function of Vitamin K
vitamin K plays an important role in the body is blood clotting or controlling. However, vitamin K can also help with:
- It decreases the risk of heart disease
- bone health
- It produces the amount of calcium in the blood
Source of vitamin K

- Source of vitamin k
- Kale
- Liver
- Spinach
- Parsley
- Butter
- egg
- Yolks
Recommended intake
You can diet of vitamin K according to your age and body requirement. Bellow some guideline has given that how to take the amount of vitamin K?
- Baby aged 0–6 months: 2 mcg
- Baby aged 7–12 months: 2.5 mcg
- children aged 1-3 years: 30 mcg
- For children aged 4–8 years: 55 mcg
- children aged 9–13 years: 60 mcg
- Child aged 14-18 years: 75 mcg
- adult women: 90 mcg
- adult men: 120 mcg
Symptoms lack of Vitamin K

- Symptoms of Vitamin K
If a person has a vitamin K lack, they have more risk of extra bleeding and low bone density that can lead to fractures.
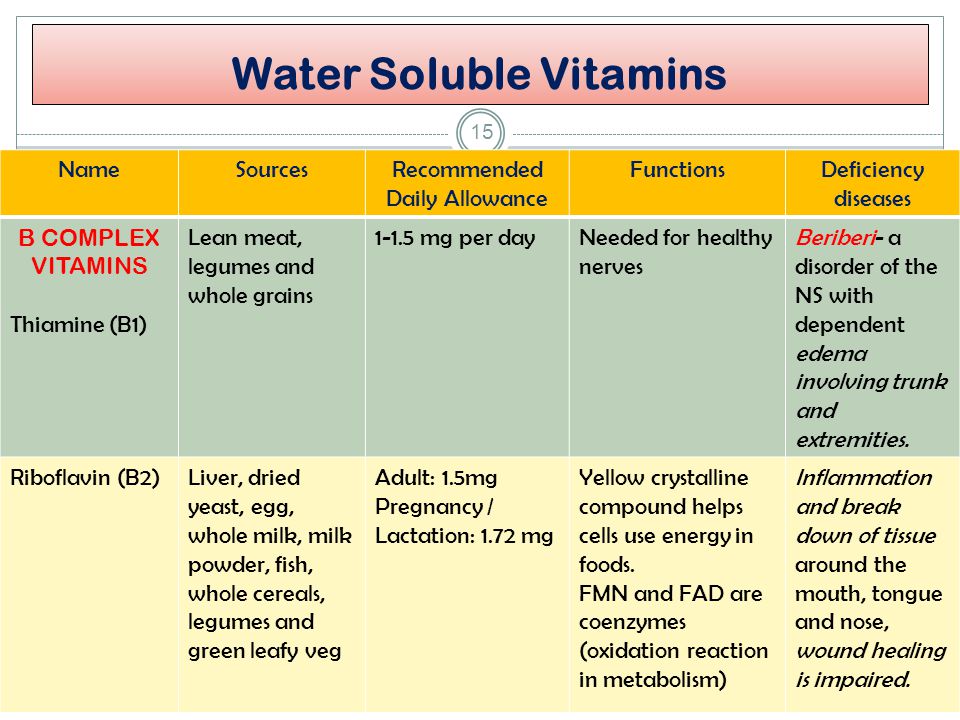
Water-soluble vitamins

- soluble vitamins in water
Water-soluble vitamins are easily solutes into the water also with this vitamin easily absorbed by the body. For example Water-soluble ( vitamin B complex and vitamin C).
1. Vitamin B1
Vitamin B1 is thiamine, which is assent the body to use glucose as energy. It is necessary for glucose metabolism and rummy a key role in nerve, muscle, and cardiac function. Vitamin B1 is a water-soluble vitamin, as are all B vitamins.
Source of the vitamin B1
1. Powdered milk
2. Oats
3. Oranges
4. Legumes
5. Pork and seeds
2. Vitamin B2
We know vitamin B2 as vitamin riboflavin. It assists to cracks down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins for the body to use. Its role in keeping an energy supply for the body is crucial. Because it helps change carbohydrates into adenine triphosphate. A compound is necessary to store energy in the tissues.
Source of the vitamin B2
1. Dairy products
2. Brewer’s yeast
3. Brussels sprouts
4. Wheat germ
5. Wild rice and mushrooms
3. Vitamin B3
As we know vitamin B3 is Niacin. This is an important nutrient. In fact, every part of your body requires to operate properly. As a supplement, niacin can help lower cholesterol, decrease arthritis and increase brain function, with other benefits.
Source of the Vitamin B3
1.Yeast,
2. Meat
3. Poultry
4. Red fish
5. Cereals and legumes.
4. Vitamin B5
We know vitamin B5 as pantheistic acid. It is the most important for human life. It is necessary to produce blood cells and helps you convert the food you eat into energy. Vitamin B5 is one of eight B vitamins. All B vitamins help you convert the proteins, carbohydrates, and fats you eat into energy.
Source of the Vitamin B5
1. Liver and kidney,
2. Yeast
3. Egg yolk
4. Broccoli
5. Peanuts and fish
B vitamins are also required for
- Healthy skin, Hair, Eye
- proper functioning of the nervous system or liver
- healthy digestive tract
- making red blood cells, which carry oxygen throughout the body
5. Vitamin B6
Vitamin B6 is a water-soluble vitamin, we are known as pyridoxine vitamin. Which means it decomposes in water. It is not stored by the body and is excreted in the urine, so people should take vitamin B6 every day. It is a member of the combined B group of vitamins. Other functions of pyridoxine combine protein and glucose metabolism, and the assembling of haemoglobin. Haemoglobin is a part of red blood cells. Which carries oxygen. Vitamin B6 is too puzzled in keeping lymph nodes, thymus and spleen healthy.
Source of Vitamin B6
1. Seafood
2. Poultry
3. Eggs
4. Dairy products
5. Leafy greens
6. Vitamin B7
Vitamin B7 known as biotin. The human body cannot manufacture biotin. Only bacteria, mold, yeasts, algae and certain plants can produce it, so the food must supply it. Extra biotin is decreased in the urine, so the body does not store reserves. It necessity be used daily. Biotin sequels are widely accessible in health food stores. But biotin loss is rare, and there is insufficient evidence to suggest that most people require them.
Source of Vitamin B7
1. Walnuts
2. Peanuts
3. Cereals
4. Milk
5. Egg yolks
Conclusion
It’s Good to have knowledge about vitamin. Because sometimes symptoms appear due to deficiency of vitamins. We have enlisted enough information about water-soluble vitamin and fat-soluble-vitamin. Because, as you know that vitamin has an important role to maintain your health. Micro nutrients of the vitamin are necessary for the human body.
Such information you must read and share with your loved ones..